The automotive industry is undergoing a revolution. With the rise of electric vehicles, autonomous driving, and advanced driver-assistance systems, the demand for skilled automotive engineers has never been higher. If you have a passion for cars and technology, a career in automotive engineering can be both rewarding and lucrative. But what qualifications do you need to succeed in this competitive field?
This comprehensive guide delves into the essential Automotive Engineering Qualifications, exploring the educational pathways, technical skills, and personal attributes needed to thrive in this dynamic industry. Whether you’re a high school student considering your options or a professional looking to upskill, this article will provide valuable insights to steer you in the right direction.
Understanding Automotive Engineering: A Blend of Disciplines
Automotive engineering is a specialized branch of engineering that focuses on the design, development, manufacturing, and testing of automobiles, including passenger cars, trucks, motorcycles, and other vehicles. It’s a multidisciplinary field, drawing upon principles from:
- Mechanical Engineering: At its core, automotive engineering heavily relies on mechanical engineering principles for designing vehicle systems like engines, transmissions, suspensions, and braking systems.
- Electrical Engineering: With the increasing electrification of vehicles, electrical engineering expertise is crucial for developing electric motors, battery systems, power electronics, and advanced control systems.
- Electronic Engineering: Modern vehicles are essentially computers on wheels. Electronic engineers contribute to the design of sophisticated engine control units (ECUs), sensors, actuators, and infotainment systems.
- Software Engineering: The automotive industry is witnessing a surge in software-driven features, from advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) to autonomous driving capabilities, demanding skilled software engineers to develop and integrate these complex systems.
- Materials Science: Automotive engineers leverage materials science to select and utilize lightweight yet durable materials, such as high-strength steel, aluminum alloys, and composites, to improve fuel efficiency and safety.
Essential Automotive Engineering Qualifications
The specific qualifications for automotive engineering roles can vary depending on factors such as the job level (entry-level, mid-level, senior-level), industry sector (OEMs, suppliers, research institutions), and specialization area (powertrain, chassis, electronics). However, certain fundamental qualifications are generally required:
1. Educational Background: Laying the Foundation
-
Bachelor’s Degree: A bachelor’s degree in automotive engineering is the most common educational pathway. However, related engineering degrees, such as mechanical, electrical, or electronics engineering, are often accepted, especially if they include relevant coursework or specializations in automotive-related subjects.
-
Master’s Degree (Optional): While not always mandatory, a master’s degree in automotive engineering or a related field can provide a competitive advantage, especially for those aspiring to pursue specialized roles or research-oriented positions.
-
Specialized Programs: Look for programs that offer specializations in areas like vehicle dynamics, powertrain engineering, automotive electronics, or autonomous vehicle technology.
2. Technical Skills: The Tools of the Trade
-
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software: Proficiency in CAD software, such as CATIA, SolidWorks, or AutoCAD, is essential for creating and modifying 3D models of vehicle components and systems.
-
Simulation and Analysis Software: Automotive engineers utilize simulation tools like MATLAB, Simulink, or ANSYS to analyze vehicle performance, optimize designs, and conduct virtual testing.
-
Vehicle Dynamics and Control: A strong understanding of vehicle dynamics principles, including suspension design, steering systems, and braking systems, is crucial.
-
Powertrain Technologies: Knowledge of internal combustion engines, transmissions, hybrid powertrains, and electric vehicle technologies is highly valued.
-
Automotive Electronics and Software: Familiarity with automotive communication protocols (CAN, LIN, FlexRay), embedded systems, and software development tools is becoming increasingly important.
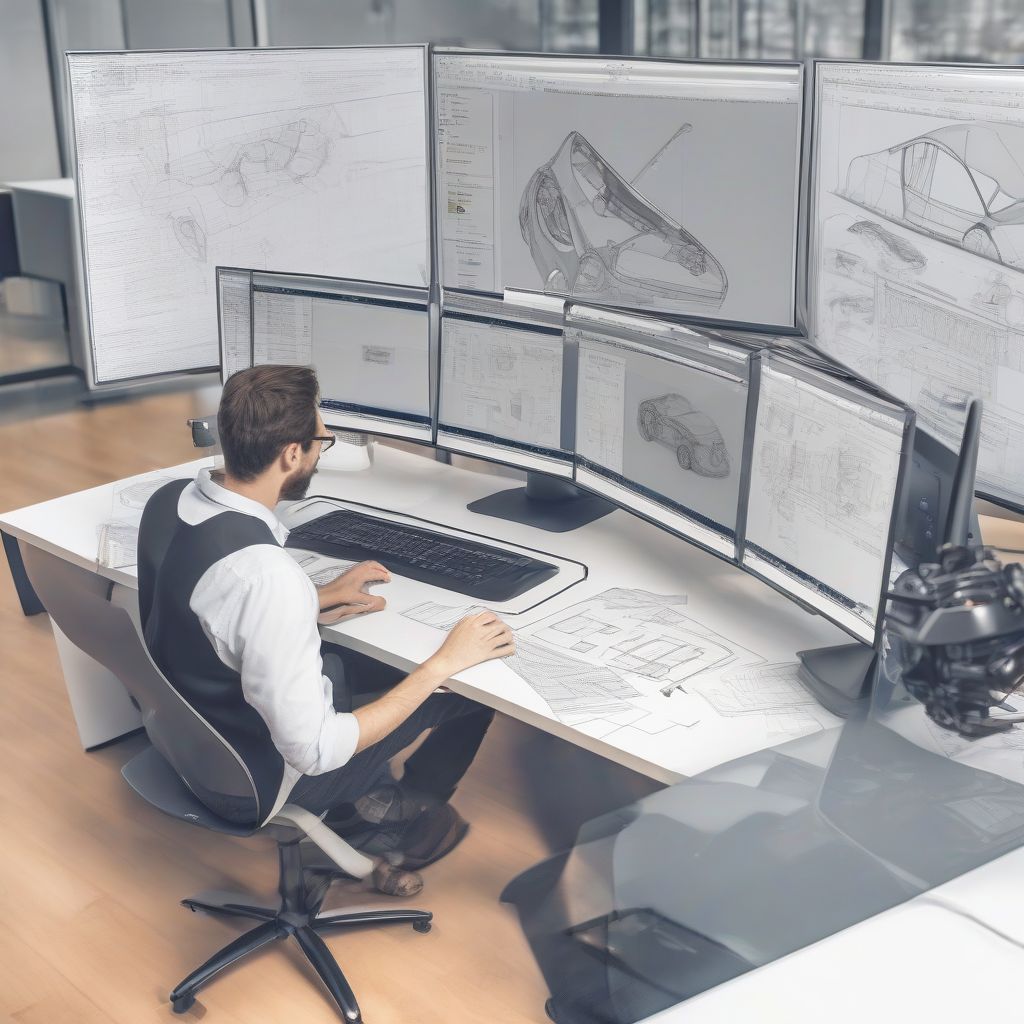 Automotive Engineer Designing an Electric Car
Automotive Engineer Designing an Electric Car
3. Personal Attributes: Beyond Technical Prowess
-
Problem-Solving Abilities: Automotive engineers are frequently tasked with solving complex technical challenges, demanding excellent problem-solving and analytical skills.
-
Communication Skills: Effective communication is key for collaborating with team members, presenting technical information clearly, and interacting with clients or stakeholders.
-
Teamwork and Collaboration: Automotive engineering projects often involve large, multidisciplinary teams, requiring strong teamwork and interpersonal skills.
-
Adaptability and Continuous Learning: The automotive industry is constantly evolving, necessitating an openness to new technologies and a commitment to ongoing professional development.
Exploring Automotive Engineering Career Paths
With the right qualifications, the automotive industry offers diverse career paths, each with unique challenges and rewards:
1. Design and Development
- Vehicle Dynamics Engineer: Focuses on optimizing the handling, stability, and ride comfort of vehicles.
- Powertrain Engineer: Develops and improves engines, transmissions, and alternative powertrain systems.
- Chassis Engineer: Designs and analyzes the structural components of a vehicle, including the frame, suspension, and steering system.
- Automotive Electronics Engineer: Works on electronic systems such as engine control units (ECUs), sensors, actuators, and infotainment systems.
2. Manufacturing and Production
- Manufacturing Engineer: Oversees the efficient production of vehicles and components, optimizing processes and ensuring quality control.
- Quality Engineer: Ensures that vehicles and components meet strict quality standards through testing, inspection, and data analysis.
3. Research and Development
- Research Engineer: Conducts cutting-edge research on new automotive technologies, such as autonomous driving, electric vehicles, and advanced materials.
Staying Ahead of the Curve: Continuous Learning
The automotive industry is in a constant state of flux, with new technologies and trends emerging rapidly. To stay competitive, automotive engineers need to embrace continuous learning:
- Professional Certifications: Certifications from organizations like SAE International (Society of Automotive Engineers) can demonstrate expertise in specialized areas.
- Industry Conferences and Workshops: Attending conferences and workshops provides valuable opportunities to stay abreast of the latest advancements and network with fellow professionals.
- Online Courses and Webinars: Numerous online platforms offer courses and webinars on specific automotive engineering topics, allowing engineers to upskill or gain expertise in new areas.
Conclusion: A Rewarding Road Ahead
A career in automotive engineering can be both challenging and immensely rewarding. By acquiring the right qualifications, embracing continuous learning, and nurturing a passion for innovation, aspiring engineers can drive their careers forward in this dynamic and evolving industry. As the automotive landscape continues to transform, the demand for skilled and adaptable engineers will only intensify, making it an exciting time to be a part of shaping the future of mobility.